Abstract
Introduction:
While randomized clinical trials (RCT) remain the gold standard for evaluating the safety and efficacy of treatments, interest in the use of external control arm (ECA) has grown when randomization is either infeasible or unethical (Friends of Cancer Research 2019). ECAs can provide contextual evidence to support regulatory approval in such situations. Single arm trials in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) is one example due to the rarity of the disease and lack of standardized treatment in this patient population. The target trial framework (Hernán and Robins 2016) can be used to emulate a hypothetical RCT that ideally would have been performed to estimate the relative efficacy of treatment of interest when non-interventional studies were used to supplement single arm trials. We present an ECA in order to contextualize the efficacy of tisagenlecleucel in the single arm Phase 2 ELARA trial with evidence on standard of care (SOC) derived from the Flatiron Health Research Database (FHRD).
Methods:
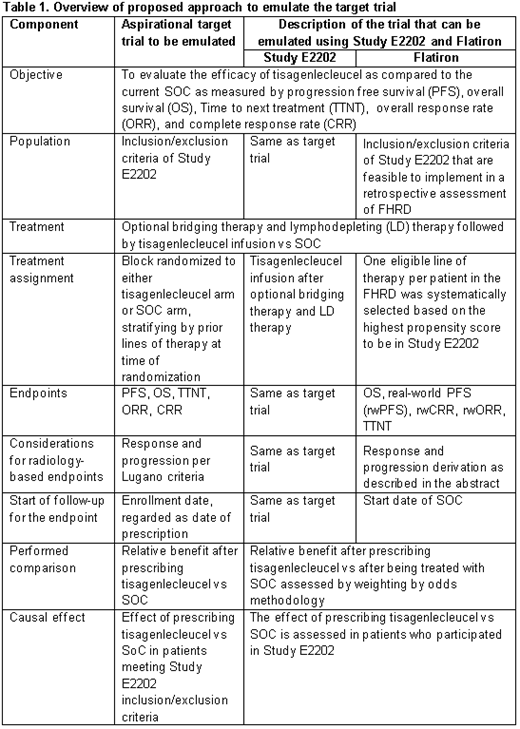
Key components of the target trial include objective, population, treatment assignment, endpoints, start of follow-up period, performed comparison and causal effect of interest. These components were specified collaboratively with clinical and statistical input. The ECA was constructed by applying key eligibility criteria from the ELARA trial to FHRD. Key endpoints including real-world progression and real-world response of the target trial were identified and curated for ECA for comparison with ELARA by reviewing clinically relevant aspects for the population/disease of interest, understanding routine documentation practices of oncology healthcare professionals at both the system level (e.g., across various hematologic and oncologic diseases) as well as at the disease specific level (e.g., NHL), and extracting from the electronic health record (EHR) specific measurements of interest. A performance assessment was conducted to confirm the comparability of real-world and trial endpoints. Methods utilizing propensity scores were used to select a single line of therapy for patients from FHRD, ameliorate the impact of measured confounding and facilitate accurate estimation of the primary causal estimand. Feedback on the proposed indirect comparison was sought a priori from the European Medicines Agency (EMA). Upon feedback from EMA, the ECA was constructed and the causal estimand of interest was assessed.
Results:
The target trial is defined in Table 1. Feasible eligibility criteria from ELARA were applied to FHRD. Briefly, the ECA included patients diagnosed with FL who had at least two prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 and alkylating agent and had not received a clinical study drug, anti-CD19, gene therapy or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Patients were aged at least 18 years at time of treatment and had at least 3 months of follow up. Some criteria from the trial could not be implemented.
Endpoints included real-world response (rwR) and real-world progression (rwP). rwR was defined as the treating clinician's assessment of radiological response based on the assessment of the burden of FL disease over the course of treatment with a given regimen. rwP was defined as an evaluation by the treating clinician of progression in FL disease after systemic treatment. The performance assessment confirmed that the rwR/rwP data can be reliably captured and that the scan frequency for rwR is similar to ELARA.
EMA acknowledged the limitations associated with the use of this ECA for indirect comparison including limited sample size, inability to match on certain inclusion/exclusion criteria, impact of missing data, potential misalignment on endpoint definition and unmeasured confounders. However, EMA recognized the usefulness of the ECA in contextualizing the efficacy of tisagenlecleucel in the current therapeutic landscape provided statistical analyses were used to address the limitations as far as possible. Detail results of this indirect comparison are included in a separate ASH abstract.
Conclusion:
Noting the limitations, an ECA constructed using EHR was considered useful to supplement and contextualize the clinical efficacy of tisagenlecleucel vs SOC from a single arm clinical trial using propensity score based methodologies to account for confounders.
Hao: Novartis: Current Employment. Hsu: Novartis: Consultancy. Parzynski: Novartis: Consultancy. Lobetti Bodoni: Novartis: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Gilead: Other: Travel sponsorship in June 2019; Spouse: F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Spouse: NHS: Ended employment in the past 24 months; Spouse: Sanofi: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Spouse: Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Spouse: Harlcok Healthcare: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Spouse: Celgene: Honoraria; Spouse: Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Spouse: Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Hampson: Novartis: Current Employment. Masood: Novartis: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Rhodes: Novartis: Consultancy. Wu: Novartis: Consultancy.
Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) an autologous CD19- directed CAR-T-cell therapy, has been approved for children and young adults with relapsed/refractory (r/r) acute lymphoblastic leukemia and, adults with r/r diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal